What Is Data Encryption?
By Laurie Robb · August 20, 2025
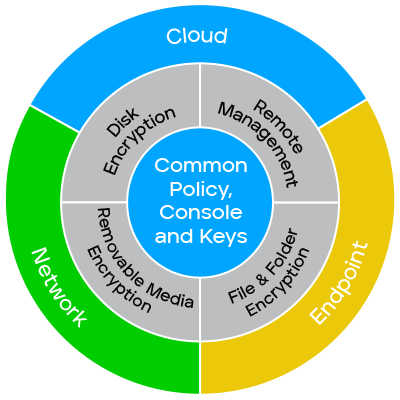
Data encryption is a fundamental component of data security that uses algorithms to transform data into an unreadable format, called "ciphertext," which can be accessed only with the correct decryption key. This process is crucial for protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, modification, disclosure, or theft across various endpoints, removable media, networks, and the cloud.
Navigating the Shift to
Post-Quantum Cryptography
Quantum computing is coming. Are you prepared?
Why is data encryption important?
Data encryption is essential for any organization, as it addresses a variety of modern cybersecurity challenges:
- Protects Data From Unauthorized Access. Encryption makes data unintelligible to anyone without the key, ensuring that if a device is lost or stolen, the information on it remains secure from brute-force attacks.
- Ensures Compliance. Many regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, mandate strict data security measures. A strong encryption solution provides the necessary evidence and audit logs to help organizations meet these compliance requirements.
- Combats Insider Risk. Users are less likely to inadvertently share sensitive information with unauthorized parties when encryption is applied. Functions like role-based access control, auto-encryption based on data loss prevention (DLP) rules, can keep information out of the wrong hands.
- Protects Intellectual Property. Device and file encryption provide a vital defense against intellectual property loss, as breaches resulting from lost and stolen devices are on the rise. As assets become increasingly mobile, the content stored on laptops, removable drives, and moving across networks can be easily compromised.
How does data encryption work?
Data encryption operates by applying algorithms to data in different states of its lifecycle:
- Data at Rest. This includes data stored on hard drives, laptops, desktops, and removable media. Encryption solutions protect this data by encrypting the entire drive or specific files and folders.
- Data in Motion. This refers to data actively being transferred over networks, sent via email, or shared through the web. Encryption ensures that this data remains protected during transit.
- Data in Use. This is data that is being actively accessed or processed. File and removable media protection solutions, for example, can protect data from unauthorized removal or exfiltration from corporate devices while being used.
Types of encryption solutions
Symmetric Cryptography. This utilizes a cryptographic algorithm that employs the same secret key to both encrypt and decrypt data. For example, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm uses a single key to scramble a message, and then unscrambles it, ensuring that only someone with that specific key can access the content.
Asymmetric Cryptography. This uses a pair of keys to secure data. A public key is used to encrypt a message or create a digital signature. A different, secret private key is used to decrypt the message or verify the signature. Examples of asymmetric encryption include RSA and ECC.
Examples of encryption algorithms
Common symmetric encryption algorithms
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). AES is a symmetric encryption algorithm that uses a single, shared secret key for both encrypting and decrypting data. AES was established as a widely recognized standard by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) in 2001 to secure everything from Wi-Fi networks to file storage. It processes data in 128-bit blocks, with longer keys (at least 256 bits) recommended for higher security.
Common asymmetric encryption algorithms
- Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA). RSA is an asymmetric encryption algorithm that uses a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. Its security relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers. Named after its inventors Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman, RSA is resource-intensive and slower than symmetric algorithms like AES. It’s commonly used to secure data in transit, like web traffic.
- Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). ECC is a form of asymmetric encryption that relies on the mathematical properties of elliptic curves to create a logarithmic challenge. It can be more efficient and secure than older algorithms like RSA. ECC uses less CPU power and memory while creating a key that is as or more computationally complex than the RSA algorithm.
Data encryption best practices
- Authentication. Based on the security goals of the organization and the type of encryption solution, set up a user sign-in that includes interaction with an authentication prompt. This should include a pre-boot verification step for the strongest security possible on endpoint devices. There are many options for multifactor authentication, including smart cards, that will make it nearly impossible for an attacker to access sensitive information, even if they have the encryption key.
- Passwords. When user passwords are part of the authentication process, especially for an endpoint device, ensure that minimum password standards are created and that the user cannot use a default password. Password synchronization with identity systems can minimize user impact.
- Access Control. This can define who has access to sensitive information and create an important “separation of duties” that limits exposure to critical information while supporting compliance with regulatory standards. Using directory integrations to assign users and groups will make the process consistent and less work for administrators.
- Device Status and Monitoring. Use of dashboards and reporting can help administrators ensure that devices are in compliance with encryption standards. When devices are not in compliance with policy, they can be identified and removed from the corporate network until appropriate action is taken.
- End User Education and Empowerment. Encryption setup should include a message to end users upon login that communicates essential policy information about their device and the protection being applied. In addition, users should be able to recover their credentials through self-service activities should they be locked out of their devices. Authorized users must be able to access their information with minimal disruption. If recovery processes are difficult or require intervention from technology services, strong encryption will be less widely adopted, making critical information more vulnerable to attacks.
Why data encryption may fail to protect you
- Key Management Issues. If encryption keys are weak, stolen, or improperly stored, the encryption will become useless. This can include using easily guessed keys, failing to rotate keys regularly, and vulnerabilities from malicious insiders or external attackers who gain access to the keys.
- Brute-force Attacks. If a system uses a weak encryption key, it’s more vulnerable to a brute-force attack, where the threat actor attempts every possible key until they find the one that works. This is an ineffective method to compromise strong keys (ex 256-bit), but it is still a concern for those organizations using more basic cryptography.
- Implementation and Maintenance Challenges. Like all technology solutions, encryption technology requires a strong implementation program, vigilant monitoring, and updates to the supporting software platforms that manage the solutions. Migrating to new solutions or updating the existing algorithms should include a plan for how the sensitive data will be handled, including the transfer of any existing keys.
- Advances in Quantum Computing. Quantum computers process vast amounts of data and solve certain complex problems exponentially faster than a conventional supercomputer. That means that as quantum technology advances, the current algorithms that keep encrypted data safe will be more easily compromised and eventually totally broken. Organizations will need to begin an immediate transition to more secure keys and an agile cryptography approach to mitigate this threat.
Industry trends: The shift to post-quantum cryptography
The cybersecurity landscape is on the verge of a significant change due to advances in quantum computing, which pose a threat to current encryption standards. This has led to the emergence of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) as a vital area of focus for organizations.
The threat of "Q-Day" and quantum algorithms
The term "Q-Day" refers to the time when a quantum computer will be powerful enough to break today's standard encryption. While the exact timing is uncertain, security professionals believe it could happen within a decade or sooner.
This has given rise to the threat of "harvest now, decrypt later" (HNDL) attacks, where adversaries collect encrypted sensitive data today to decrypt it once powerful quantum computers become available. According to a recent survey, a significant majority of organizations, around 65%, are concerned about this threat.
The two main quantum algorithms that threaten current cryptography are:
- Shor's Algorithm. This algorithm targets asymmetric cryptography like RSA and ECC by efficiently solving the mathematical problems they rely on. This will require the replacement of these algorithms with new ones.
- Grover's Algorithm. This generic quantum search algorithm affects symmetric cryptography, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). It can reduce the effective strength of a symmetric key by half; for example, reducing AES-128 to a 64-bit strength. For this reason, organizations should target a minimum of AES-256 to retain adequate protection.
The move to quantum-resistant cryptography
To counter these threats, the industry is shifting to new families of mathematical problems that are difficult for both classical and quantum computers to solve. A leading approach is "lattice-based cryptography."
NIST is leading the standardization effort and has selected new algorithms such as CRYSTALS-Kyber for key establishment and CRYSTALS-Dilithium for digital signatures.
Crypto agility and organizational readiness
The ability to efficiently update cryptographic algorithms without significant disruption, known as cryptographic agility or crypto agility, is crucial for this transition. This requires more than just swapping algorithms; it involves a thorough cryptographic inventory and strategic research.
Organizations should ensure they have immediate and long-term resourcing plans to support their transition to crypto agility, with processes and technologies that address this fundamental threat to data security.
The CyberThreat Report
Insights gleaned from a global network of
experts, sensors, telemetry, and intelligence
Trellix’s approach to data encryption
Trellix provides a comprehensive approach to data encryption that is managed through a centralized ePolicy Orchestrator (ePO) platform. This platform allows for the easy deployment and administration of encryption policies across endpoints and removable media.
- Centralized Management. Trellix’s ePO console allows you to manage encryption policies for all devices, including native OS encryption, from a single location. This workflow simplifies compliance and streamlines administration.
- Flexible Policies. The solutions offer an extensive catalog of policy options to secure information across devices, files, and removable media, as well as to define access control for users and groups.
- User Self-service. Trellix Data Encryption products include user recovery options that reduce help desk support calls by allowing users to regain access to their devices through challenge questions or other self-service methods.
- PQC Transformation. Trellix is integrating cutting-edge PQC into its data encryption products, including collaborating with wolfSSL to work toward FIPS 140-3 validation for the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) environment, where authentication occurs at system boot.
Types of Trellix data encryption solutions
Trellix offers a suite of encryption products that can be used individually or combined to provide comprehensive data protection:
- Trellix Drive Encryption (TDE). TDE is a proprietary full-disk encryption solution for Windows devices that uses strong access control with pre-boot authentication (PBA). It supports multi-user environments, Active Directory integration, and multifactor authentication (MFA) to provide a higher level of security than native encryption.
- Trellix Native Drive Encryption (TNE). This solution centralizes the management of native encryption features like Microsoft BitLocker and Apple FileVault. It allows administrators to monitor encryption status, collect and manage keys, and ensure compliance from a single console.
- Trellix File & Removable Media Protection (FRP). FRP safeguards sensitive data from being removed from corporate devices by encrypting files, folders, and removable media. It also enables users to securely share data with external parties and recover access to protected data if needed.
By implementing a robust data encryption strategy, organizations can effectively protect their data, meet compliance requirements, and reduce the risks associated with data breaches and insider threats.
Data encryption FAQ
- Protects Data From Unauthorized Access: Makes data unintelligible without the key, securing information even if a device is lost or stolen.
- Ensures Compliance: Helps organizations meet strict data security measures mandated by regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
- Combats Insider Risk: Reduces the likelihood of users inadvertently sharing sensitive information by applying encryption and using features like role-based access control and auto-encryption based on DLP rules.
- Protects Intellectual Property: Device and file encryption protect assets stored on laptops and removable drives, and when moving across networks.
- Data at Rest: Data stored on hard drives, laptops, desktops, and removable media is protected by encrypting the entire drive or specific files/folders.
- Data in Motion: Data being transferred over networks, sent via email, or shared through the web is encrypted to ensure it remains protected during transit.
- Data in Use: Data actively being accessed or processed is shielded from unauthorized removal or exfiltration using file and removable media protection solutions.
- Authentication: Establish a step to verify the user. Incorporate this activity before the system boots for endpoint devices, and set up multifactor authentication for enhanced security.
- Passwords: Create minimum password standards and prevent the use of default passwords. Minimize user impact by synchronizing passwords with identity systems.
- Access Control: Define who has access to sensitive information to limit exposure and support compliance with regulatory standards. Use directory integrations to assign users and groups.
- Device Status and Monitoring: Use dashboards and reporting to ensure devices are in compliance with encryption standards and to identify/remove noncompliant devices.
- End User Education and Empowerment: Communicate essential policy information to users upon login. Provide self-service options for credential recovery to minimize disruption.
- Key Management Issues: Weak, stolen, or improperly stored encryption keys can render encryption useless.
- Brute-force Attacks: In this scenario, the threat actor attempts every possible key until they find the one that works.
- Implementation and Maintenance Challenges: Effective use of encryption technology requires a strong implementation program, vigilant monitoring, and timely updates to supporting software platforms.
- Advances in Quantum Computing: Quantum computers could potentially break current encryption algorithms, necessitating a transition to more secure keys and an agile cryptography approach.
Data encryption resources

Trellix Drive Encryption safeguards data and devices from unauthorized access.

Get protection that meets government and industry standards and ensures that files are encrypted when transferred to removable media or sent via email.

Learn how a multilayered data encryption strategy protects sensitive data and helps prevent catastrophic leaks.
Laurie Robb leads Product Marketing for Trellix Data Security. Her product lines include Data Loss Prevention, Data Encryption, and Database Security. She has more than two decades of marketing communications experience with specialities in corporate technology, SaaS software, and cybersecurity solutions.