What Is GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is EU legislation passed on May 25, 2018 that is designed to give individuals more control over their personal data—defined as any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person—and to establish a single set of data protection rules across the European Union. To comply with this new data protection act, companies must “implement appropriate technical and organizational” measures to protect personal data. These measures include:
- Knowing what data they hold and have appropriate rights to use the data
- Being able to answer questions from customers, as well as employees and former employees, about what type of data they hold, and, in some cases, delete data they no longer need
- Considering privacy and security at the start of a project or in first building a product, and do a review of projects before launching
- Notifying their main regulator within 72 hours of becoming aware if they have a security incident
- Requiring their vendors to also secure their data, and record this commitment in a contract
It’s important to note that GDPR requirements don’t just apply to EU organizations; they apply to all organizations, anywhere in the world, that target, collect, or use the personal data of any EU resident. Organizations that fail to comply with GDPR can face stiff penalties and fines—up to 2% or 4% of total global annual turnover or €10 million or €20 million, whichever is greater.
An opportunity to change the way you secure data
Delivering personal data protection to EU residents continues to be a challenge and a priority as the business, technology, and threat landscapes evolve and become more complex. Where do you begin? As a first step, assess your data loss risks. Next, take an inventory of your attack surfaces and look at how you can better protect them. Finally, you’ll want to think about how your technology transformation plans could be integrated with a GDPR security investment to deliver personal data security.
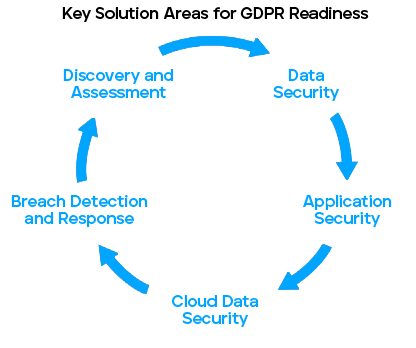
Step 1: Continuous Discovery and Assessment — Discover, classify, and inventory personal data.
Step 2: Data Security — Protect personal data at rest and in motion on endpoints and in the cloud.
Step 3: Application Security — Defend critical applications in the data center and cloud.
Step 4: Cloud Data Security — Safeguard personal data that is uploaded to the cloud, that resides in the cloud, and that is downloaded from the cloud.
Step 5: Breach and Detection Response — Ensure that critical processes are in place to detect, investigate, and remediate breaches in a timely manner.