
Trellix Global Defenders: BlackCat Ransomware as a Service - The Cat is certainly out of the bag!
By Trellix · February 8, 2022
Research Contributions and Analysis: Filippo Sitzia
This story was written by Arnab Roy
Threat Summary
Blackcat also known as ALPHV/Noberus is a Ransomware as a Service provider originally being detected around the end of November 2021. While analyzing the campaign we discovered several important aspects of this ransomware including operational similarity with previous ransomware families such as Darkside, Blackmatter and Revil. It is understood that Blackcat is potentially actively recruiting affiliates to increase proliferation and offering lucrative financial deals related to profit sharing of up to 90% in some cases.
Blackcat has potentially been attributed to a spate of recent attacks spread across various critical sectors such as energy, transportation and utilities.
This threat actor Is continuously updating their services and adding features and modifying their code to provide advanced penetration capabilities for It’s affiliates. Keeping track of this threat groups activities Is extremely crucial and organisations can stay updated by keeping an eye on the IOC's and updates being provided by the Trellix ATR team via our Threat Dashboard and Trellix Insights platform.
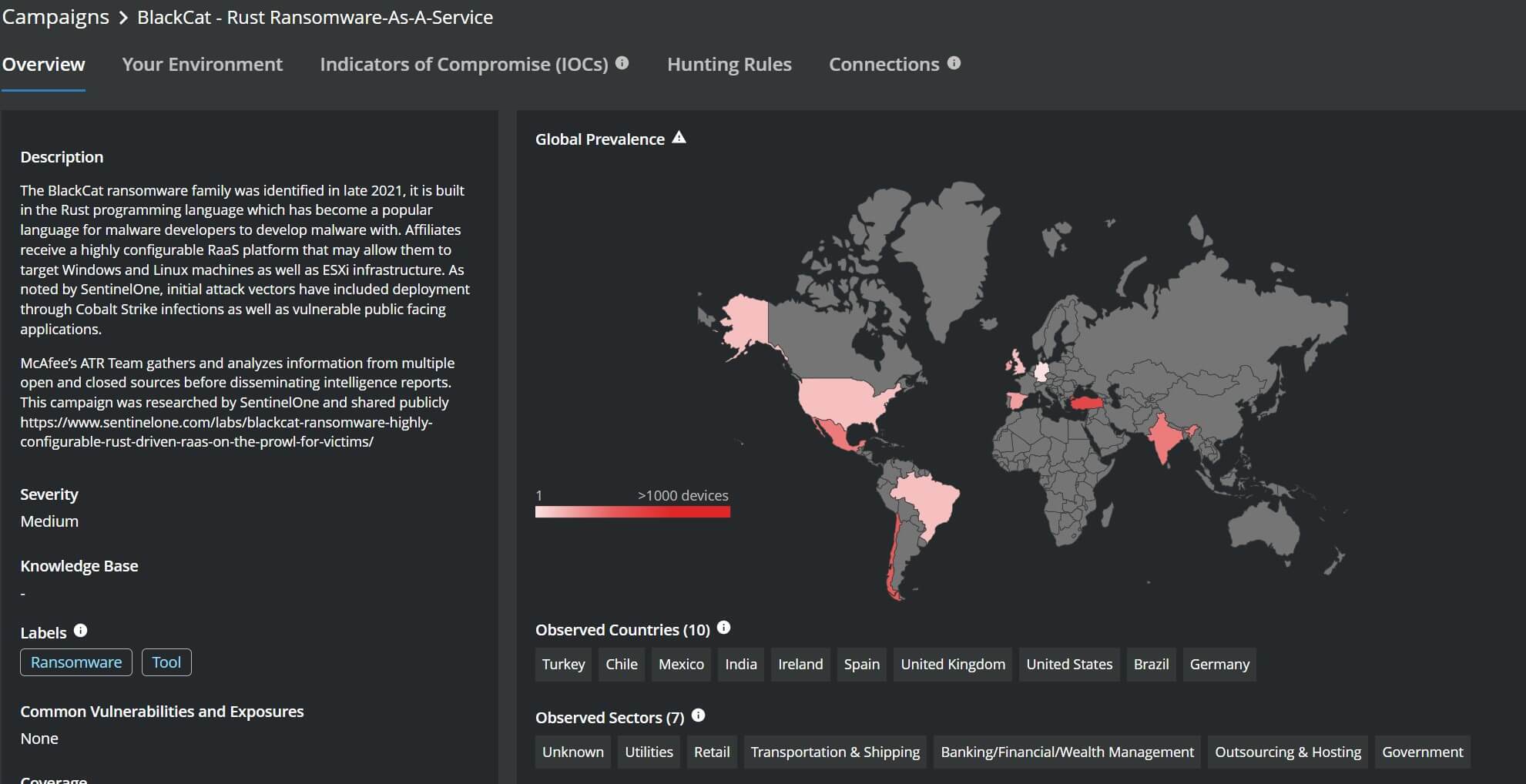
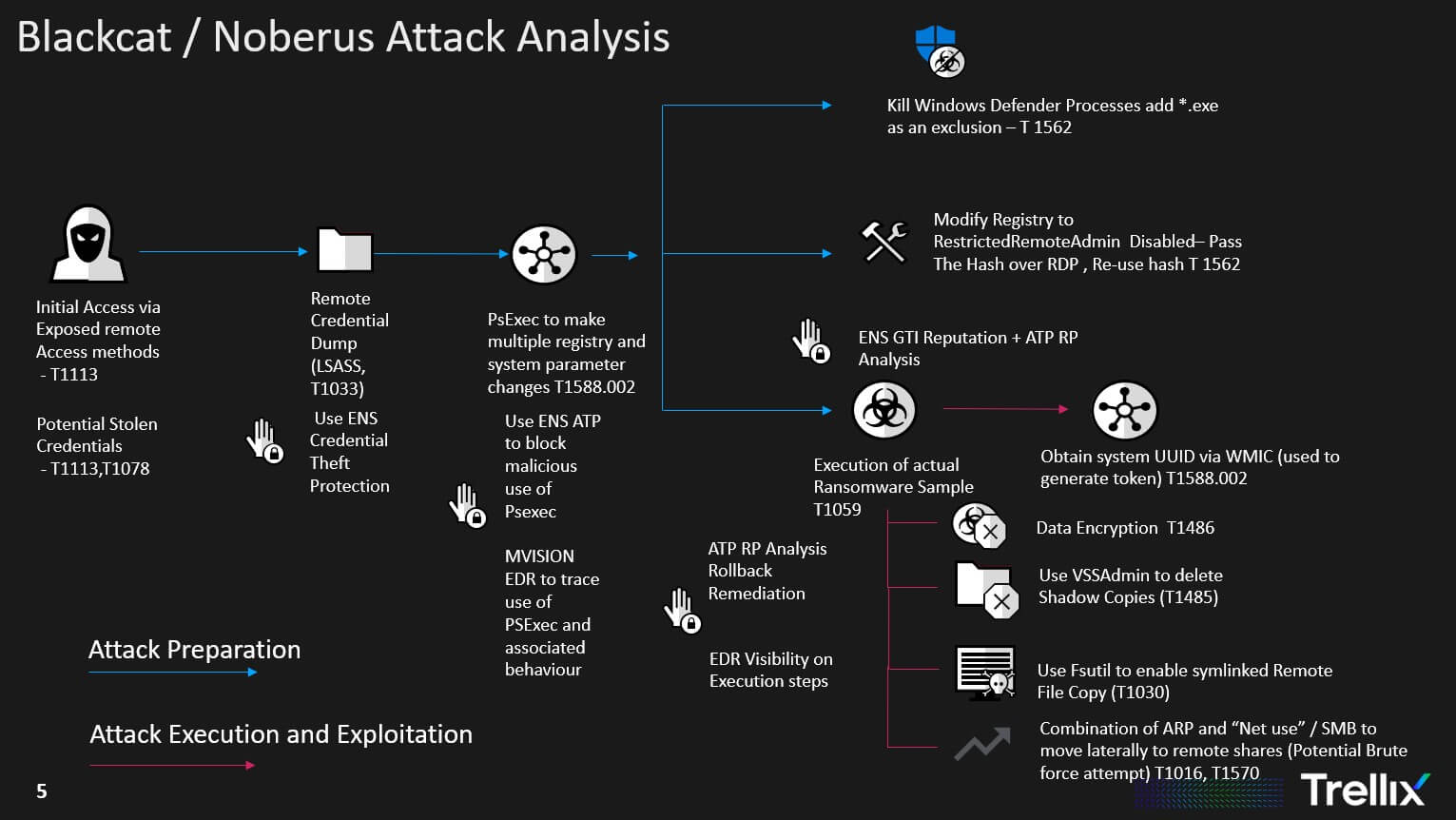
An analysis of the attack flow shows typical pre-execution and post execution stages of a ransomware incident. The initial access is gained either via leaked credentials or through exposed remote access software. Following this it is clear the threat actor spends a good amount of time compromising various defenses such as Windows Defender , enabling better data exfiltration by increasing connection limits on remote connections, discovering network shares etc. The actual encryption part seems to come at later stage similar to what we have seen with other Ransomware families such as Darkside etc.
Why Is this Important?
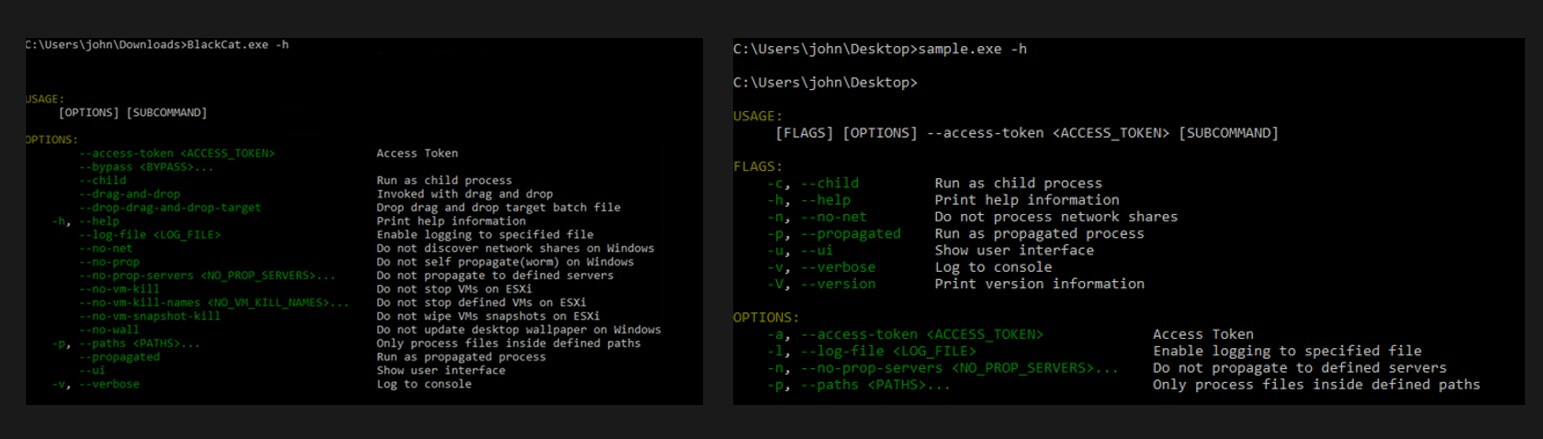
So what makes BlackCat different than previous ransomware as a service operators? the answer is many. This ransomware has been written using a programming language known as “Rust” diverging from common programing languages such as C/C++ in which previous ransomwares has been written in and is more widely understood and analyzed by threat researchers and defenders. The advantage of using “Rust” is maximum platform support in terms of OS that this ransomware can be executed on, potentially hugely widening the exposure for organisations. The next aspect is customization capabilities available in the malware and how it has embedded a lot of disparate capabilities in a modular self- contained package, it even has a help menu! Perfectly suitable for newbie affiliates. The notable capabilities include embedded PsExec, Powershell process migration capabilities and ability to infect VMWare ESXi services. The configuration options shown bellow allows the affiliates to customize how they execute the ransomware in the victims environment.
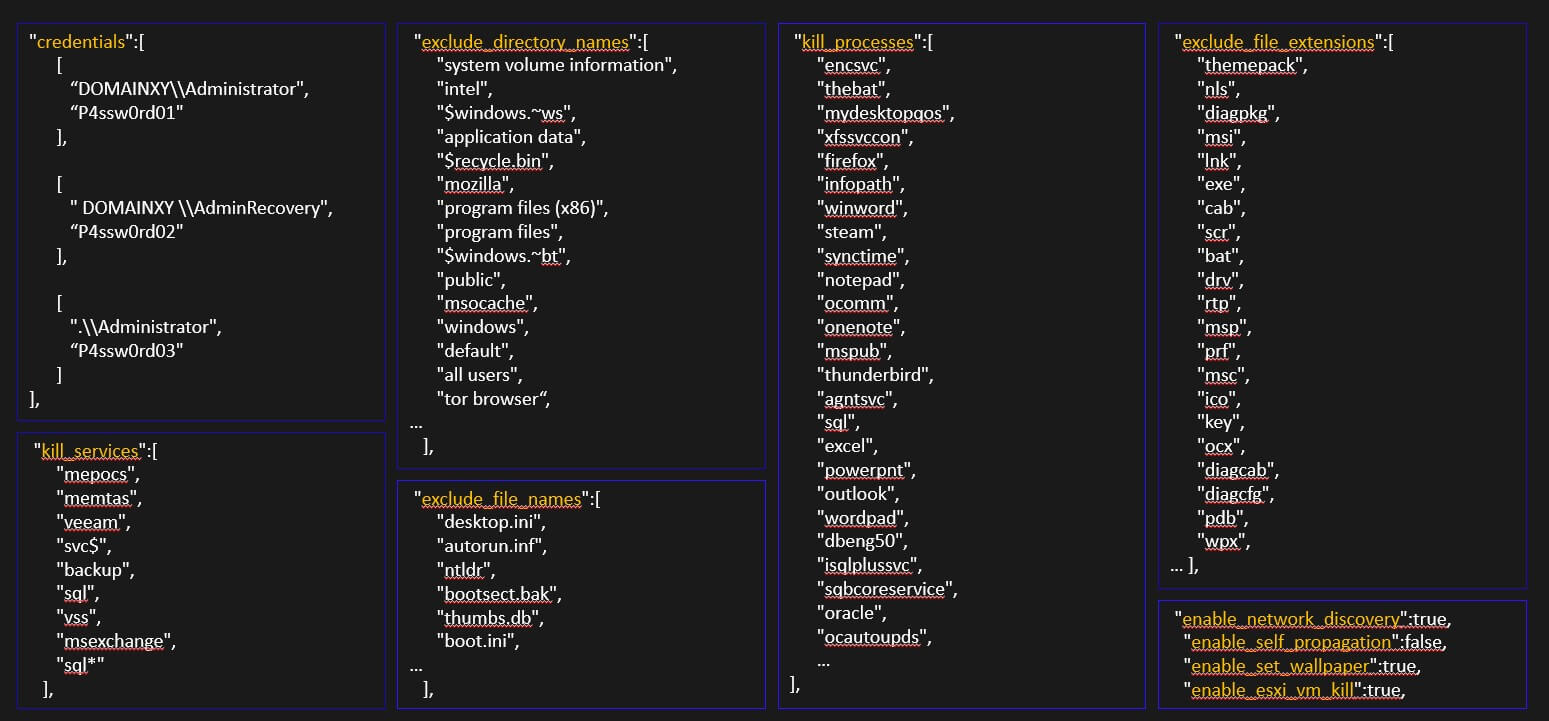
The most important aspect is possibly the fact that during analysis we discovered that each sample had configuration files embedded that included information such as Usernames and passwords for the target victims to facilitate lateral movement(potentially gathered from previous breaches or bought password dumps). We also noticed that a unique access token is used to generate an unique victim identifier and a unique link for Blackcat’s “Tor” webpage for the ransomware negotiations to take place. This is specifically designed to keep security researchers and law enforcement out of the conversations as well as defeating some automated sandboxing capabilities that does not inject sample specific attributes.
Defenders Guidance
One of the hardest part of this ransomware family is keeping track of prevalence information. The reason being that almost every sample has a different set of IOC's associated with it(hash, tor url , access tokens, config files). So this is where we have to resort to more advanced behavioral characteristics and properties of the malware. Establishing relationship between the various samples might be extremely important at an early stage of an attack to understand the threat actor and their associated tactics, a new feature added to Trellix Insights provides just that:
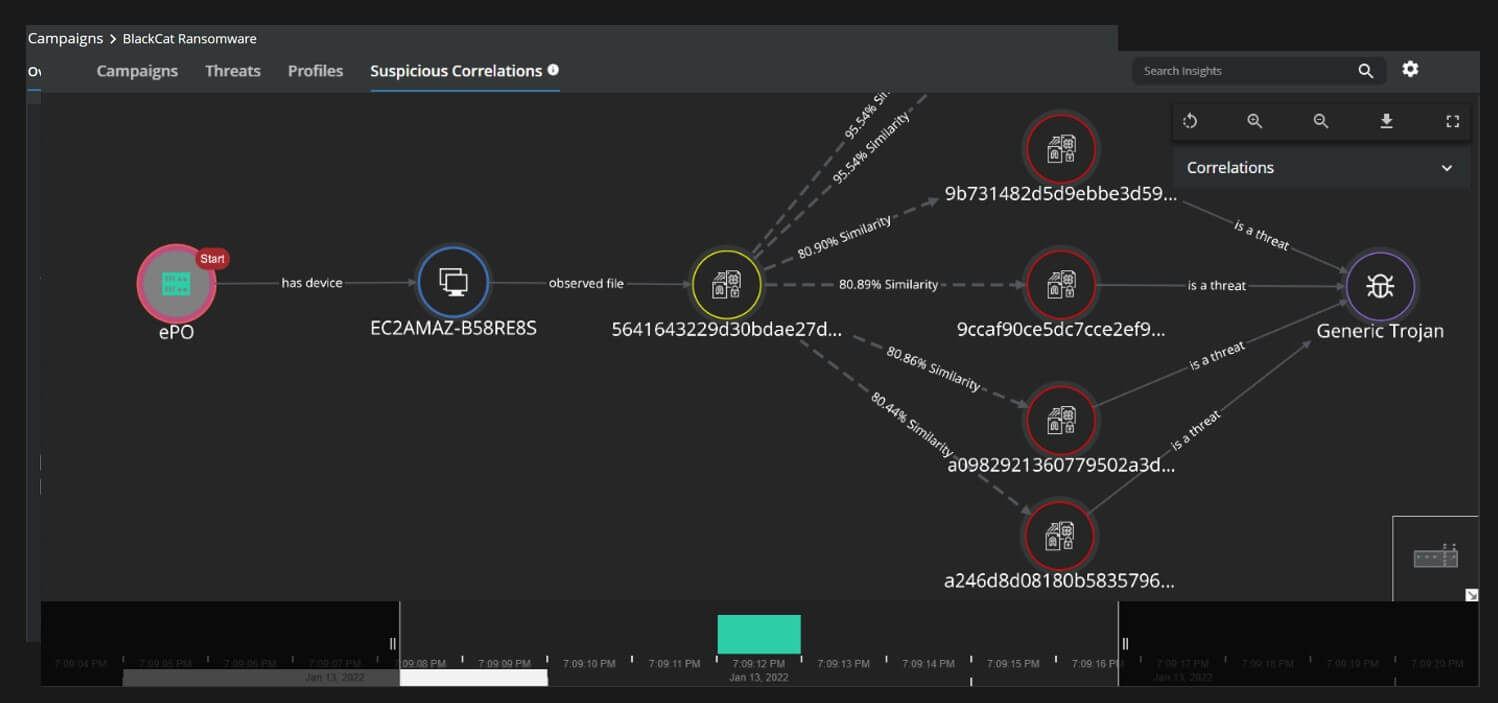
Like with every ransomware attack the signs of the presence of the threat actor are visible In the early part of the attack lifecycle. Use of LOLBins and Dual Intent tools to land and expand are critical signals that should be captured by defenders, both EDR and ENS ATP provides early visibility Into the pre-execution phase of the attack as well as Post execution phases.
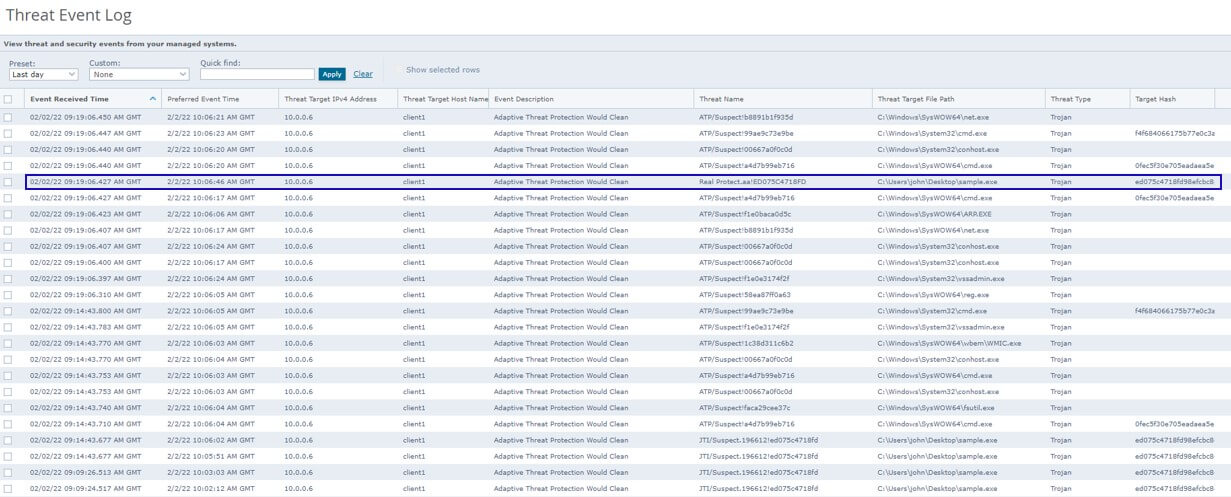
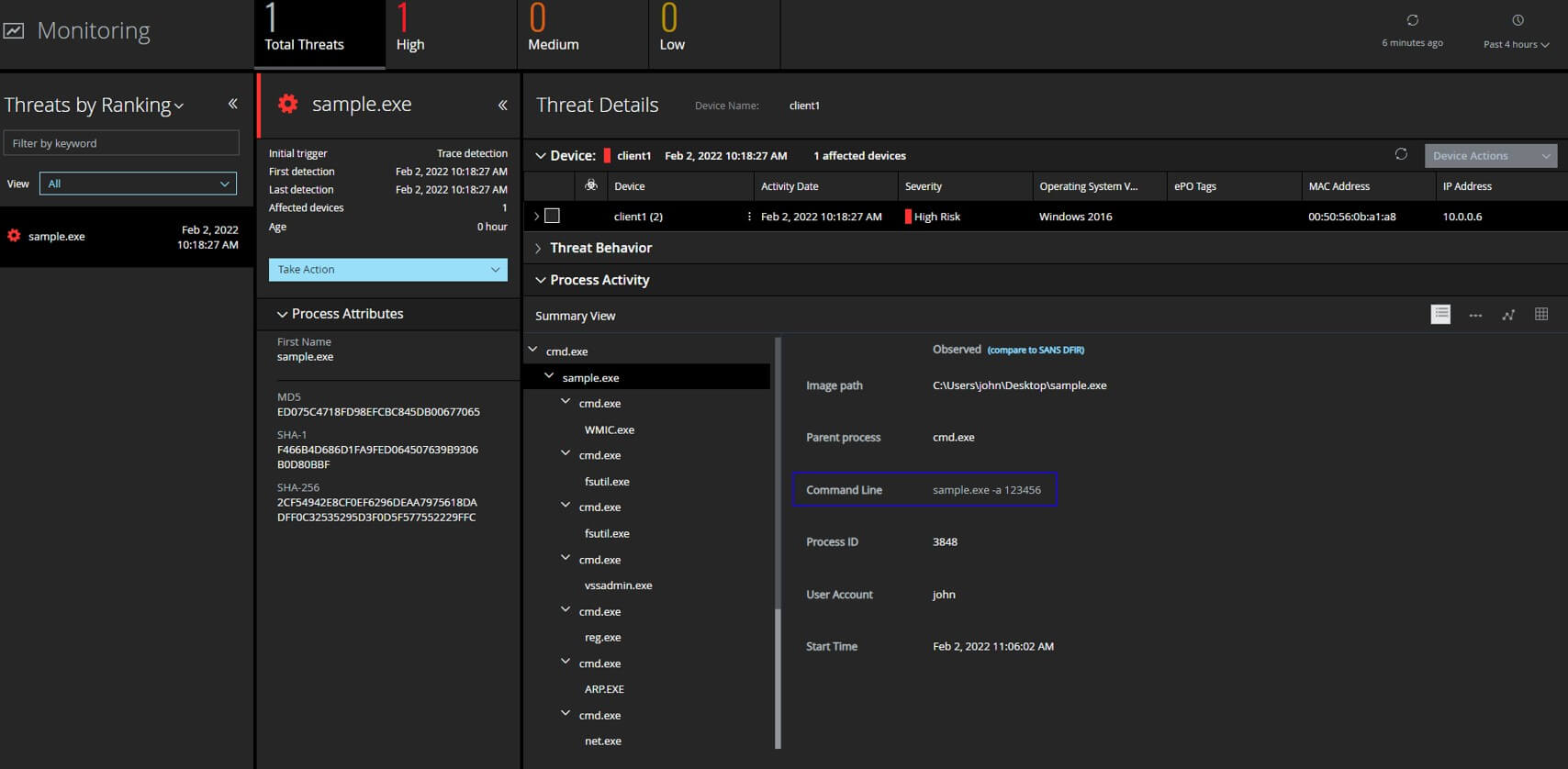
Point to be noted here is that depending on the sample the data collected EDR trace analysis could appear differently. Having behavioral analysis and protection capabilities is critical for defenders during our testing both ENS Realprotect static and cloud got trigged and Enhanced remediation recovered the encrypted systems successfully.
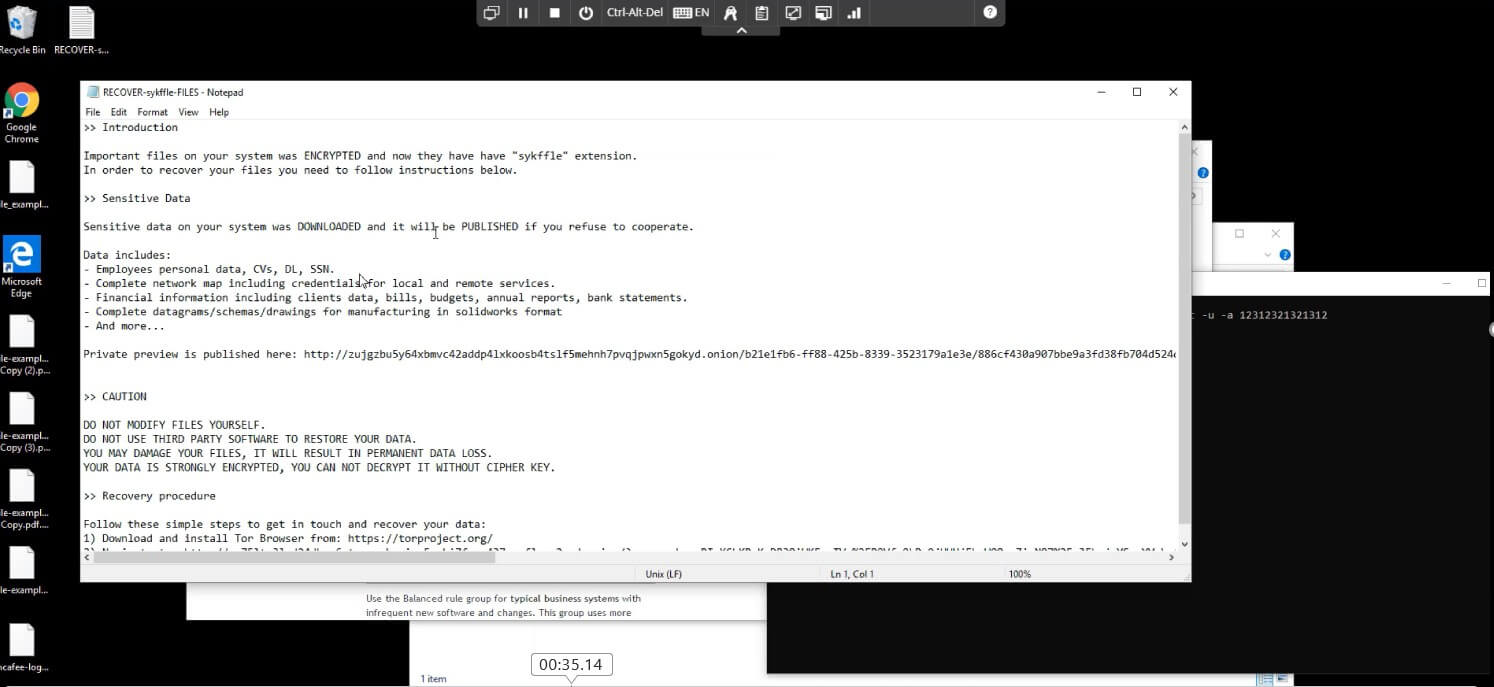
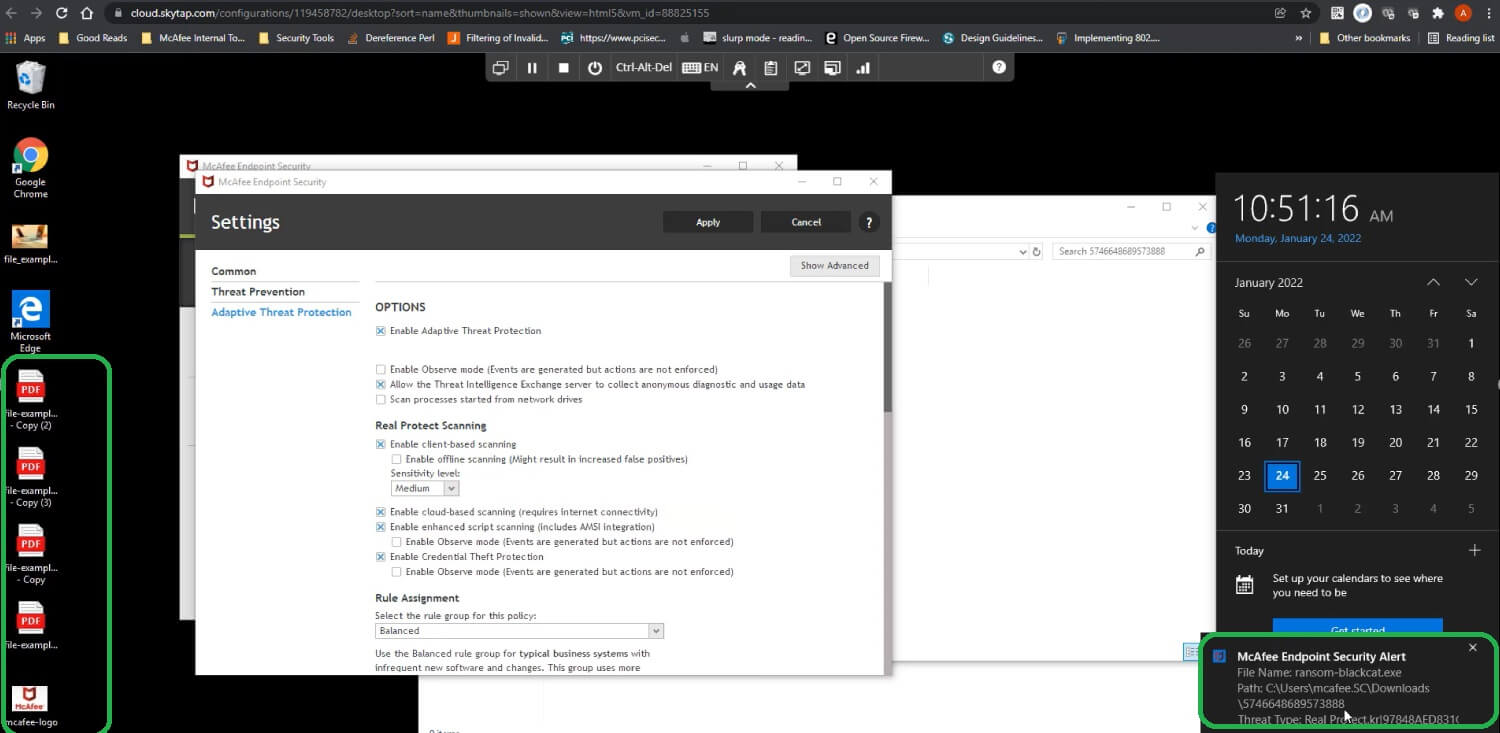
Being able to analyze threats fully and understand its behavior is crucial especially in a malware that is changing its attributes rapidly, Trellix Detection on Demand provides additional sampling capability along with endpoint integration to further enhance defenses and detection capabilities.
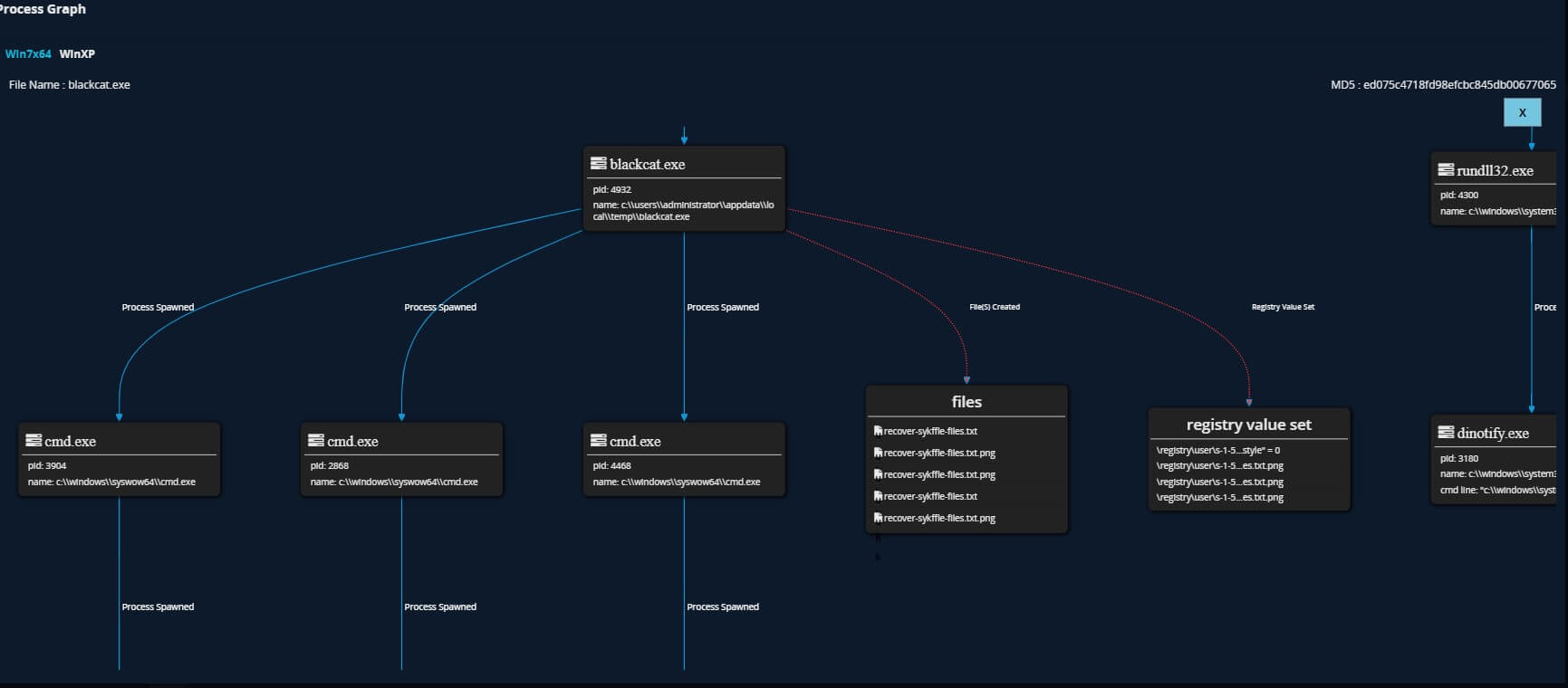
Summary
Organisations need to build resilient defenses against ransomware threats and not rely on single control/defenses, we can expect to continue to see more innovation from threat actors such as the ones highlighted here, fundamentally the following provides an effective security strategy against ransomware threats
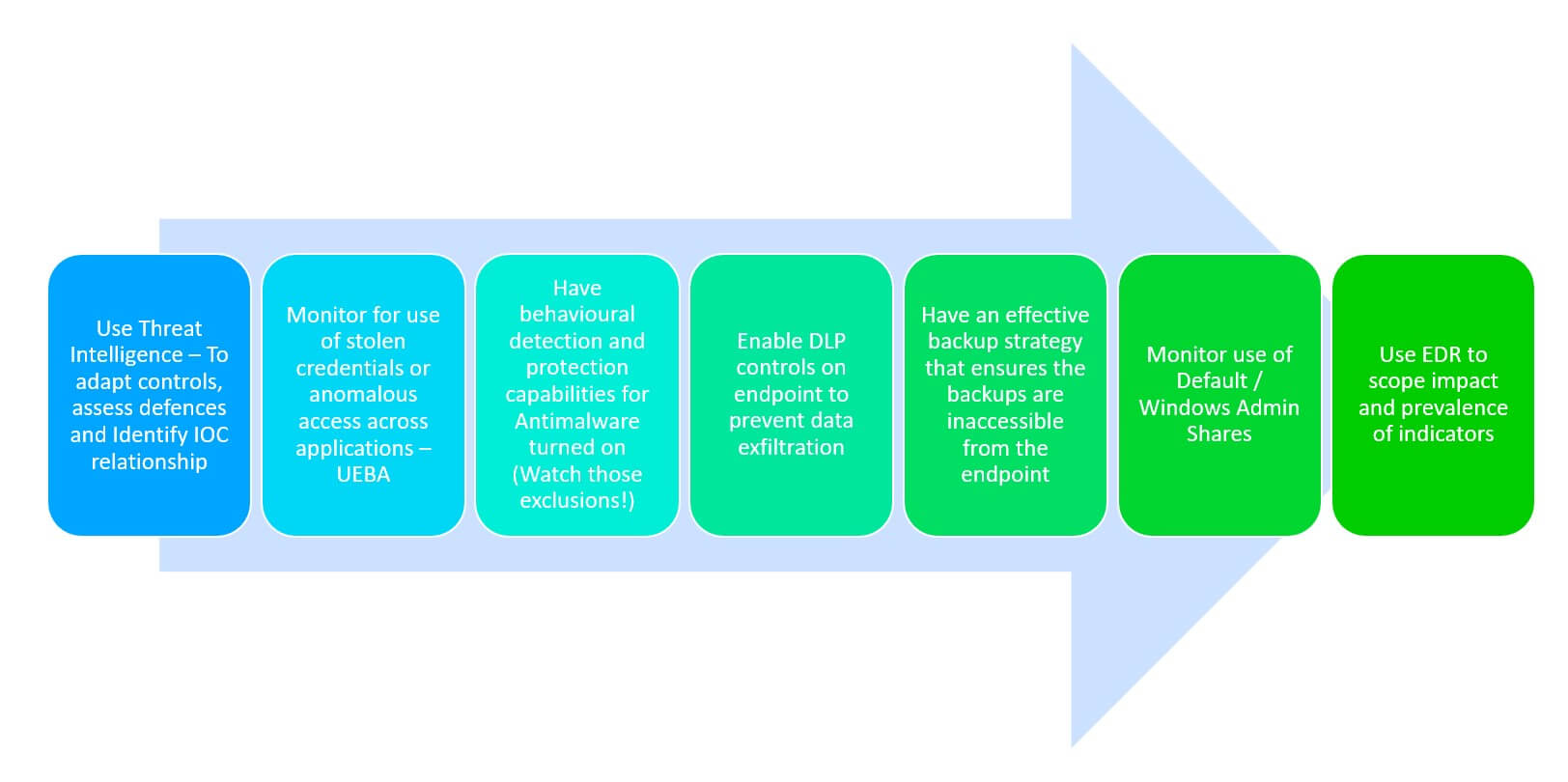
RECENT NEWS
-
Jun 17, 2025
Trellix Accelerates Organizational Cyber Resilience with Deepened AWS Integrations
-
Jun 10, 2025
Trellix Finds Threat Intelligence Gap Calls for Proactive Cybersecurity Strategy Implementation
-
May 12, 2025
CRN Recognizes Trellix Partner Program with 2025 Women of the Channel List
-
Apr 29, 2025
Trellix Details Surge in Cyber Activity Targeting United States, Telecom
-
Apr 29, 2025
Trellix Advances Intelligent Data Security to Combat Insider Threats and Enable Compliance
RECENT STORIES
Latest from our newsroom
Get the latest
Stay up to date with the latest cybersecurity trends, best practices, security vulnerabilities, and so much more.
Zero spam. Unsubscribe at any time.