Blogs
The latest cybersecurity trends, best practices, security vulnerabilities, and more
The Democratization of Phishing: Popularity of PhaaS Platforms on the Rise
By Ryan Slaney · June 30, 2025
The phishing industry is being profoundly reshaped by the surge of Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) platforms. These accessible, often Artificial Intelligence (AI)-powered, offerings are democratizing sophisticated phishing attacks, making them available to a wider audience with limited technical skill. Platforms such as Darcula, Morphing Meerkat, Lucid, EvilProxy, Tycoon 2FA, Sneaky 2FA, Rockstar 2FA, ONNX, and Greatness, to name a few, are fundamentally altering the threat landscape, enabling cheaper, easier, and more effective phishing campaigns.
Why PhaaS is surging in popularity
PhaaS platforms appeal to cybercriminals for several reasons. They lower technical barriers with intuitive dashboards, templates, and automation, enabling novices to launch sophisticated attacks quickly. Cost-effectiveness is a key driver, as subscription models offer a high return on investment compared to custom infrastructure. PhaaS platforms provide enhanced anonymity and evasion through features like IP blocking, dynamic URLs, and leveraging legitimate communication channels (e.g., iMessage, RCS) to bypass traditional security. Their inherent scalability and automation allow for managing thousands of phishing pages and high-volume message distribution with minimal effort. This competitive landscape also fuels continuous innovation, as providers constantly update features and evasion methods.
PhaaS kits are specifically designed to offer easy-to-use, often highly polished, administrative panels. This is a core part of their appeal and a key factor in democratizing phishing attacks, making them accessible even to individuals with minimal technical skills. These panels are typically web-based interfaces that resemble legitimate Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms, complete with user-friendly navigation, clear metrics, and automated functionalities.
The alarming role of artificial intelligence
The integration of AI significantly amplifies the scale and sophistication of PhaaS attacks. AI enables automated phishing page generation, rapidly cloning legitimate websites with flawless mimicry and branding. It drives hyper-realistic content creation, crafting persuasive, grammatically perfect, and multi-lingual phishing lures tailored to specific targets. AI also facilitates dynamic and adaptive attacks, allowing campaigns to adjust in real-time based on victim behavior. Crucially, AI enhances evasion techniques, making URLs, content, and server behaviors polymorphic and harder for traditional security tools to detect.
A look at prominent PhaaS platforms and their specialties
While they share core functionalities, each PhaaS platform often has a distinct specialization or set of features that sets it apart:
- Darcula (approx. $250/month): Specializes in highly realistic, customizable SMS-based phishing (smishing), with advanced link cloaking and dynamic page generation to impersonate global brands. Often linked to the Chinese "Smishing Triad."
- Morphing Meerkat: Primarily focuses on stealing email login credentials. Its unique strength lies in its ability to perform advanced DNS reconnaissance, dynamically generating tailored login pages to match legitimate interfaces. It also employs evasion techniques like open redirects and code obfuscation.
- Lucid: Linked to the Chinese "XinXin group," its standout feature is exploiting Rich Communication Services (RCS) and Apple's iMessage protocol for sending smishing messages, bypassing traditional SMS filters. It offers real-time victim monitoring and advanced anti-detection techniques.
- EvilProxy (approx. $400/month): A highly dangerous platform with Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) capabilities and real-time Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) bypass. It acts as a reverse proxy, intercepting credentials and MFA codes or session cookies directly, making it incredibly difficult to detect.
- Tycoon 2FA: Highly effective at MFA bypass, primarily targeting Microsoft 365 and Gmail accounts. It's known for sophisticated evasion tactics, including encrypting scripts, using invisible Unicode characters for code obfuscation, and leveraging Cloudflare Turnstile to deter security researchers.
- Sneaky 2FA (approx. $150-$200/month): Another prominent AiTM phishing kit specifically targeting Microsoft 365 accounts for credential and session token theft. It features pre-populated login forms, blurred login backgrounds for realism, and bot detection evasion, often managed via a Telegram bot.
- DadSec / Phoenix / Rockstar 2FA: Often seen as evolutions, these platforms orchestrate widespread email campaigns, sometimes leveraging QR code phishing (quishing) to bypass email security. They capture credentials and session cookies for MFA bypass and are often managed via Telegram bots.
- Caffeine now ONNX (approx. $150-$250/month): Specialized in targeting Microsoft 365 accounts, particularly in the financial sector. ONNX distributes phishing attacks via PDF attachments containing QR codes and uses dynamic URL generation, providing unique phishing URLs for each victim.
- Greatness: Notable for its sleek, user-friendly interface and widespread adoption, indicating a comprehensive and effective suite for credential theft, making it highly accessible to a broad range of cybercriminals.

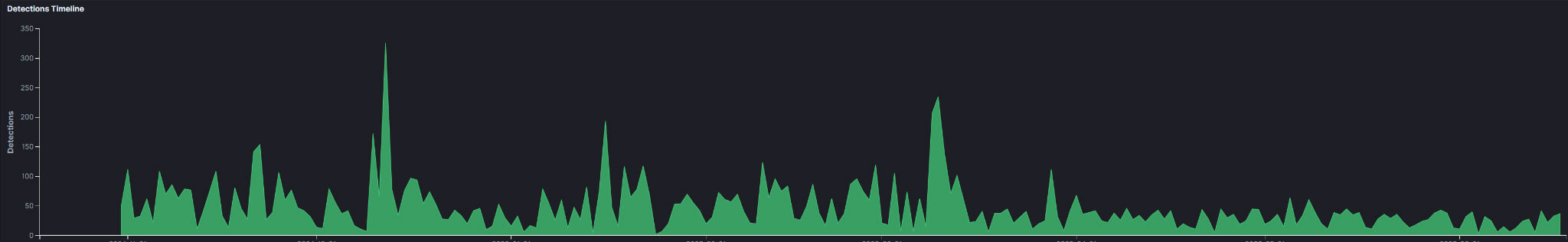
PhaaS Detection Telemetry - Morphing Meerkat
While it is difficult to to consistently and definitively detect and attribute phishing activity to a specific PhaaS platform - the very design of these services is intended to complicate such efforts, providing a layer of obfuscation for their criminal subscribers - detection telemetry of URLs known to be associated with specific PhaaS kits allows Trellix to narrow down the prevalence of any one particular PhaaS platform.
For example, since Trelix began tracking the Morphing Meerkat PhaaS in November, 2024, we have observed 10,846 detections of Morphing Meerkat-associated URLs. Detections are not indicative of a compromise, it's simply when a file, URL, IP address, or other indicator is detected by one of our products and reported back to us. Almost half of these detections (4,395) were located in the United States which indicates Morphing Meerkat affiliates are focusing their efforts on U.S.-based targets white the rest of the detection activity is spread out worldwide.

Our telemetry also reveals that nearly half (45%) of the detections were observed amongst the outsourcing and hosting sector, 35% found in the telecom sector, with the remainder spread across the process manufacturing, banking/financial/wealth management, transportation and shipping, and education sectors.

Overall, the detection data for Morphing Meerkat since November 2024 shows relatively consistent prevalence with spikes in activity observed in December 2024 and March 2025. While the overall detection rate is down in 2025 compared to 2024, this is likely due to affiliates switching to newly available competitor PhaaS platforms that offer a more attractive price point or features the affiliate is particularly interested in.
What does the future hold for PhaaS Platforms?:
Law Enforcement Interdiction
It’s unlikely that we will observe the use of PhaaS kits wane anytime soon. In fact, they are likely to become even more popular as they grow more sophisticated and effective. However, this popularity has attracted the attention of law enforcement and intelligence agencies hell bent on disrupting PhaaS schemes. For example, the international dismantling of LabHost in April 2024 struck a major blow against the PhaaS ecosystem and resulted in a significant win for law enforcement.
This coordinated, year-long operation, led by the UK's Metropolitan Police with extensive support from Europol, the FBI, and law enforcement agencies across 19 countries, successfully neutralized one of the world's largest PhaaS providers. LabHost, operational since late 2021, provided over 10,000 users with access to more than 170 customizable phishing templates, enabling the creation of over 40,000 fake websites impersonating banks, postal services, and other major organizations. The platform, which earned over £1 million (approximately $1.17 million USD) from subscriptions, allowed cybercriminals to steal over one million user credentials and nearly 500,000 credit card numbers. The operation resulted in 37 arrests worldwide, including LabHost's original developer, and saw the seizure of critical infrastructure, sending a clear message to the cybercrime community that their illicit services are not untouchable. There’s no doubt that law enforcement would like nothing more than to repeat the success of this operation against other PhaaS platforms.
Adoption by state-sponsored actors
Another possible scenario could see state-sponsored actors start to leverage PhaaS platforms to augment their existing capabilities. While state-sponsored threat actors have traditionally relied on in-house phishing capabilities, the rise of sophisticated and accessible PhaaS platforms makes it possible—and potentially likely—that these actors will integrate such services into their operations to enhance efficiency and scale.[2] This shift would allow them to conduct large-scale phishing campaigns with reduced resource investment and obfuscate their phishing activity by blending it in with other actors using the same PhaaS.
How Trellix defends against PhaaS platforms
Trellix offers a multi-layered and integrated approach to defend organizations against the sophisticated threats posed by PhaaS kits. Our Email Security solutions serve as the primary defensive line, leveraging advanced AI and machine learning (including technologies like PhishVision for image-based phishing detection and MVX for sandboxing attachments) to meticulously analyze inbound and outbound emails. This helps identify and block phishing attempts, malicious URLs (even dynamic or obscured ones), and weaponized attachments before they reach user inboxes, directly countering the initial delivery methods of PhaaS.
Should a phishing attempt bypass email filters, Trellix Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), powered by its agent and AI-guided investigations (like Trellix Wise), continuously monitors endpoint activity for suspicious behaviors indicative of post-phishing compromise, such as credential harvesting attempts, suspicious process execution, or lateral movement.
Finally, Trellix Helix Connect integrates telemetry from email, endpoints, network, and cloud environments. This holistic view enables correlation of disparate events across the entire attack chain, allowing for the rapid detection of complex, multi-stage PhaaS campaigns, including advanced AiTM attacks and credential theft, and automates responses to quickly contain and remediate threats.
Combining Trellix’s multi-layered solutions with the enforcement of phishing-resistant MFA requirements and continuous security awareness training for users represents a robust defence and mitigates the threat posed by PhaaS platforms considerably.
Discover the latest cybersecurity research from the Trellix Advanced Research Center: https://www.trellix.com/advanced-research-center/
RECENT NEWS
-
Feb 10, 2026
Trellix SecondSight actionable threat hunting strengthens cyber resilience
-
Dec 16, 2025
Trellix NDR Strengthens OT-IT Security Convergence
-
Dec 11, 2025
Trellix Finds 97% of CISOs Agree Hybrid Infrastructure Provides Greater Resilience
-
Oct 29, 2025
Trellix Announces No-Code Security Workflows for Faster Investigation and Response
-
Oct 28, 2025
Trellix AntiMalware Engine secures I-O Data network attached storage devices
RECENT STORIES
Latest from our newsroom
Get the latest
Stay up to date with the latest cybersecurity trends, best practices, security vulnerabilities, and so much more.
Zero spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
