Blogs
The latest cybersecurity trends, best practices, security vulnerabilities, and more
How Trellix Helix detects AS-REP Roasting in Active Directory
By Adithya Chandra and Maulik Maheta · November 13, 2025
Executive Summary
Adversaries use AS-REP Roasting to extract and crack password hashes from Active Directory (AD) accounts with Kerberos preauthentication disabled, a misconfiguration that exposes credentials to offline brute force attacks. Unlike other methods, AS-REP Roasting does not require prior access to credentials or elevated privileges, making it a low-noise but high-impact attack vector.
This blog from the Trellix Advanced Research Center describes a real-world scenario in which an attacker:
- Identifies vulnerable AD accounts without preauthentication
- Requests AS-REP responses with crackable encrypted password hashes from ticket-granting tickets (TGTs)
- Uses offline tools such as Hashcat to brute-force weak passwords that are not visible to traditional security tools
Trellix Helix enhances AS-REP Roasting detection through a multilayered threat detection strategy, leveraging endpoint and network telemetry, log data, and threat intelligence. It features a dual alerting mechanism: atomic alerts that capture individual malicious behaviors, and correlated alerts that stitch together related events to reveal the bigger picture. These key capabilities are incorporated into Trellix Helix with the help of its Advanced Correlation Engine (ACE). ACE identifies and scores threat events in real-time, using both rule and risk-based logic.
Whether you are a SOC analyst, incident responder, or identity and access defender, this blog will show you how to detect AS-REP Roasting attempts early and take corrective action using Trellix Helix's powerful correlation capabilities.
What is AS-REP Roasting?
AS-REP Roasting is a post-exploitation technique that enables an attacker to obtain encrypted password hashes for specific AD user accounts with Kerberos preauthentication disabled.
In a typical Kerberos authentication flow, a user sends an authentication service request (AS-REQ) to the key distribution center (KDC) and must prove their identity (usually by encrypting a timestamp with their password-derived key) before the server returns an authentication service reply (AS-REP ) message containing a ticket-granting ticket (TGT).
When Kerberos preauthentication is disabled for a user account (a common misconfiguration for service accounts or legacy systems), the KDC sends the AS-REP containing data encrypted with the user's password hash without requiring proof of identity.
This opens up an opportunity for attackers:
- They use GetNPUsers.py or Rubeus to enumerate accounts that have preauthentication disabled
- They send specially crafted AS-REQs for those accounts
- The KDC responds with AS-REP messages that contain data encrypted with the user's password hash
- The attacker then extracts this information and cracks the hash offline with tools such as Hashcat or John the Ripper, hoping to recover the actual password
Since the cracking occurs offline, there is no risk of account lockout or detection by traditional authentication monitoring tools.
Attack Flow: Cracking Active Directory passwords with AS-REP Roasting
Figure 1 shows the entire AS-REP Roasting attack sequence, from identifying misconfigured accounts to capturing AS-REP responses and performing offline password cracking. It explains how attackers exploit disabled Kerberos preauthentication in Active Directory.
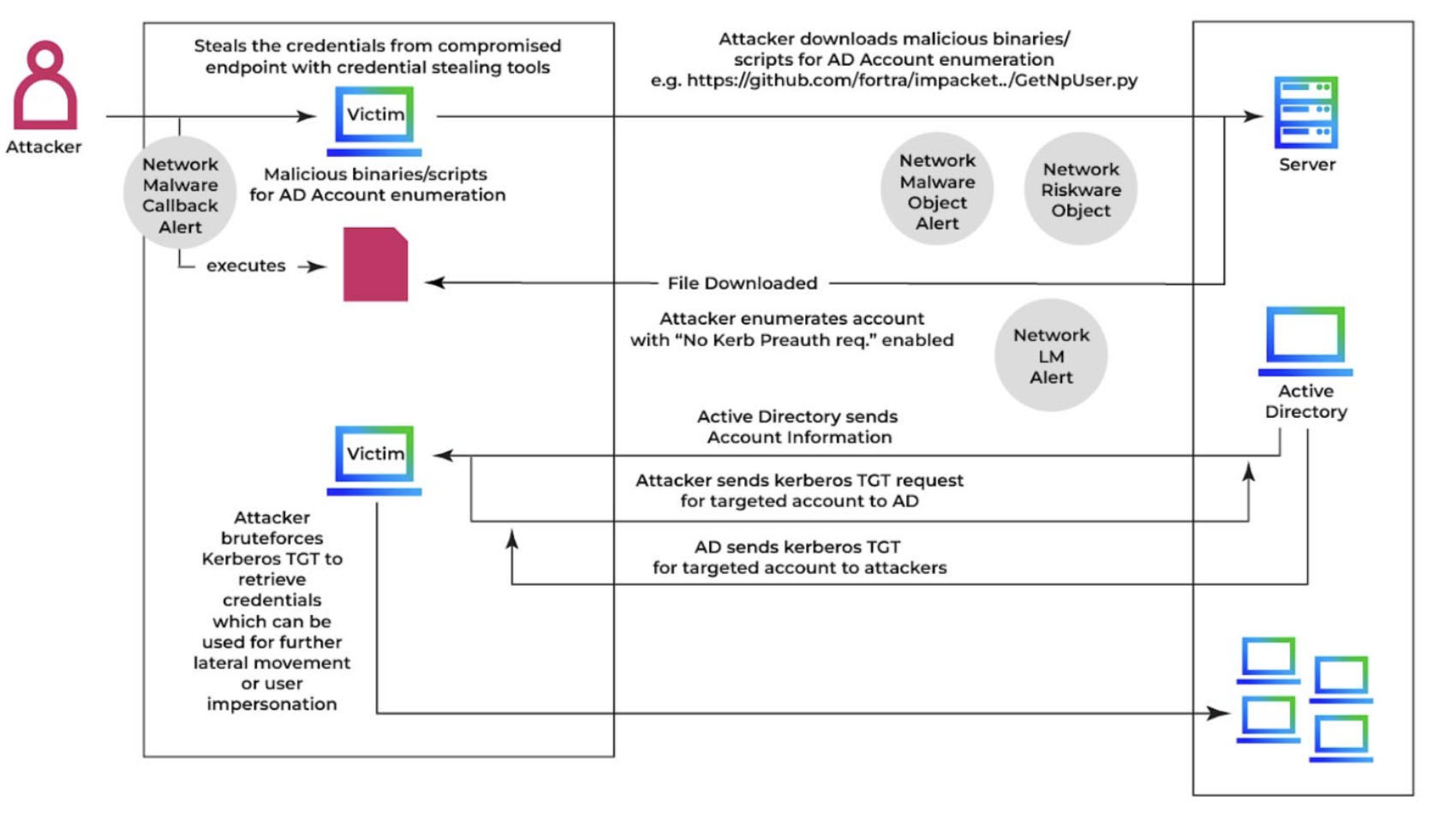
Step 1: Discover accounts with Kerberos preauthentication disabled
The attacker scans the domain to identify user accounts with Kerberos preauthentication disabled, making them vulnerable to AS-REP Roasting.
Step 2: Request TGT tickets and extract hashes
The attacker sends AS-REQ requests to the KDC, captures AS-REP responses containing encrypted password hashes, and prepares them for offline brute-force cracking using tools like Hashcat, avoiding account lockouts and detection.
For the detailed simulation steps, refer to our blog here.
Detection: Trellix Helix with Advanced Correlation Engine (ACE)
Trellix Helix provides comprehensive detection capabilities for AS-REP Roasting attacks through its Advanced Correlation Engine (ACE). ACE leverages a multilayered threat detection strategy that combines endpoint and network telemetry, log data, and native Trellix threat intelligence to identify and score threat events in real-time using both rule and risk-based logic.
Dual alerting mechanism for enhanced visibility
As attackers execute AS-REP Roasting attacks across the environment, Trellix Helixsurfaces atomic alerts aligned with each tactic or technique used. These atomic alerts capture individual malicious behaviors, such as:
- Reconnaissance of LDAP queries to identify accounts with preauthentication disabled
- Unusual volume of AS-REQ requests to domain controllers
- Kerberos service ticket requests for accounts with disabled preauthentication
- Network patterns indicating enumeration of vulnerable accounts
Security analysts can then enable the "Group Alerts" feature, which consolidates these signals into a single correlated alert, offering a clear, contextual narrative of the attacker's activity. This correlation transforms fragmented events into actionable intelligence, enabling rapid response to thwart the attack lifecycle.
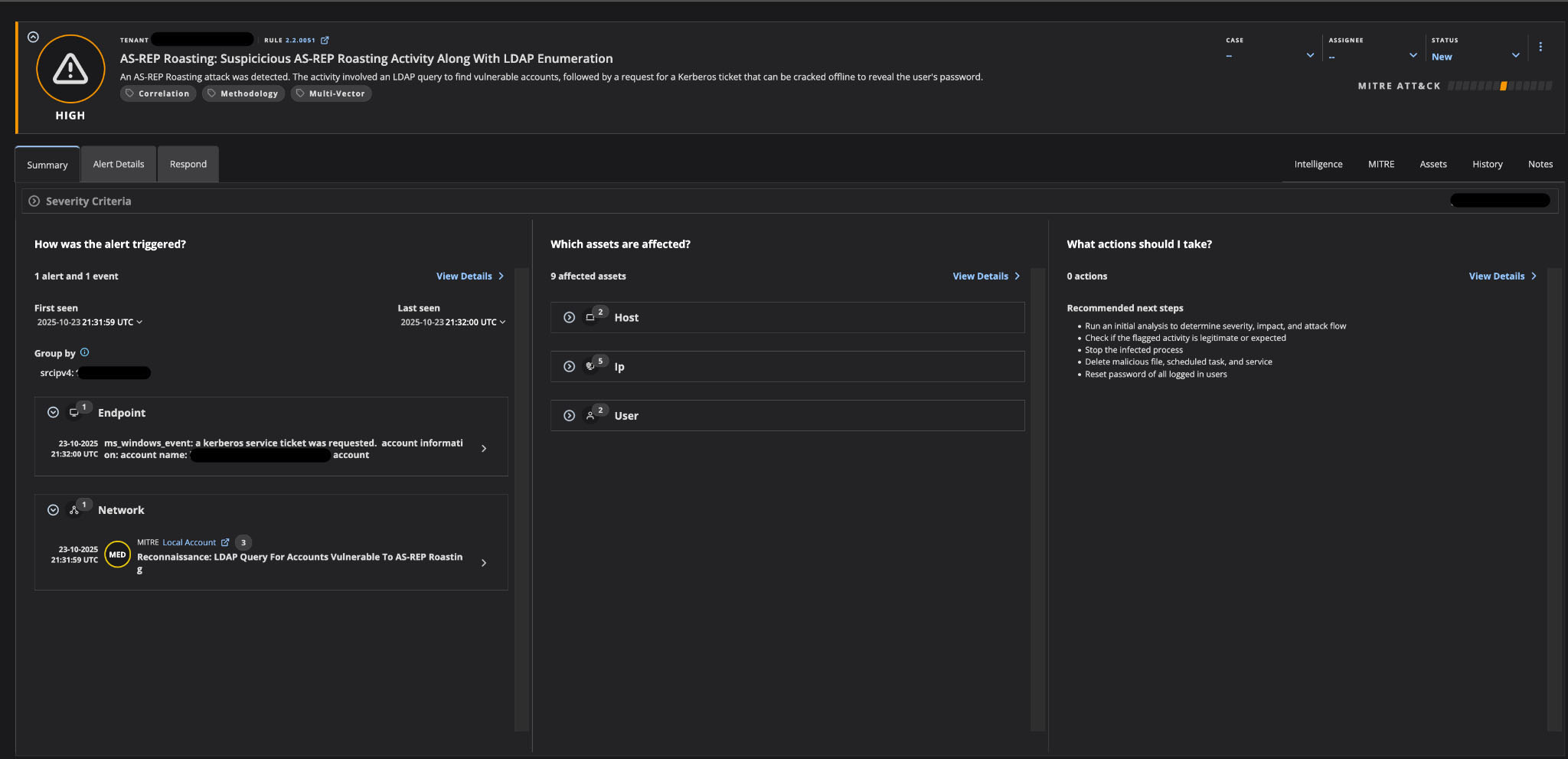
Figure 2 shows the consolidated alert view in Trellix Helix, which presents a comprehensive summary of the AS-REP Roasting attack detection.
The alert is classified as HIGH severity and titled "AS-REP Roasting: Suspicious
AS-REP Roasting Activity Along With LDAP Enumeration."
This correlated alert demonstrates Trellix Helix's ability to link multiple attack stages into a single, actionable detection. The alert description clearly identifies the attack pattern: an LDAP query was first used to discover vulnerable accounts with Kerberos preauthentication disabled, followed by a request for a Kerberos ticket containing encrypted data that can be cracked offline.
The alert provides immediate visibility into the attack scope, showing nine affected assets across multiple categories: two hosts, five IP addresses, and two user accounts. The source IP is prominently displayed, enabling rapid threat containment. Notably, the "How was the alert triggered?" section reveals the dual-layered detection: an endpoint event captured the Kerberos service ticket request for a user account, while the network alert identified the reconnaissance phase through Trellix NX's detection of the LDAP query for AS-REP vulnerable accounts. This multivector correlation, combining endpoint, network, and identity data, is a key function of Trellix Helix, providing defenders with a complete narrative rather than isolated security events.
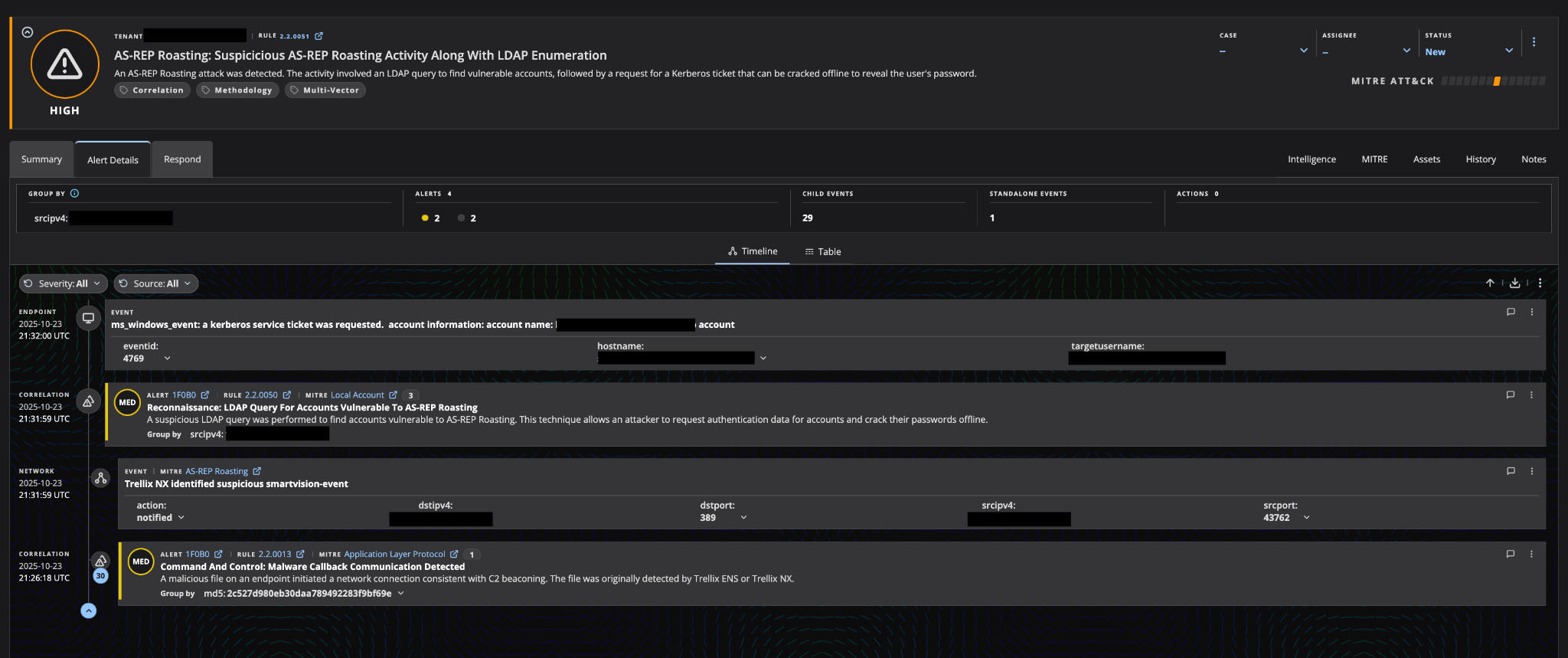
Figure 3 presents the Alert Details timeline view, which chronologically sequences the attack events to reveal the full kill chain of the AS-REP Roasting attempt. This temporal visualization is critical for understanding how the attack unfolded across different security telemetry sources. The timeline shows the attack generated atomic and correlated alerts with multiple child events, demonstrating the comprehensive visibility Trellix Helix provides into attacker activity.
This layered timeline view enables SOC analysts to trace the attacker's progression from reconnaissance through exploitation. The multivector correlation approach, combining endpoint telemetry, LDAP enumeration detection, network behavior analysis, and C2 communication patterns, enables security analysts to understand not just isolated indicators, but the entire attack chain from initial reconnaissance through credential harvesting attempts and post-exploitation activity.
Recommended next steps
Based on the Trellix Helix detection, security teams should:
- Run an initial analysis to determine severity, impact, and attack flow
- Check if the flagged activity is legitimate or expected
- Stop the infected process immediately
- Delete malicious files, scheduled tasks, and services
- Reset passwords for all logged-in users on affected systems
- Review and enable Kerberos preauthentication for vulnerable accounts
- Hunt for similar activity patterns using ACE correlation rules
ACE Correlation advantages
The Advanced Correlation Engine in Trellix Helix provides several advantages for detecting AS-REP Roasting:
- Real-time Threat Scoring with Contextual Intelligence: ACE applies risk-based scoring to events by analyzing them within their full operational context, considering user behavior baselines, asset criticality, attack progression, and environmental factors. This context-aware scoring prioritizes high-confidence detections for immediate analyst attention, ensuring AS-REP Roasting attempts targeting critical accounts receive elevated priority over routine authentication anomalies.
- Cross-product Correlations: Combines endpoint logs and network traffic to build a complete attack narrative.
- Reduced False Positives: By correlating multiple indicators, ACE filters out benign administrative activity and focuses on true attack patterns.
- Automated Context Enrichment: Each alert includes MITRE ATT&CK mappings, affected assets, user context, and recommended remediation actions.
Conclusion
AS-REP Roasting is a stealthy and effective attack technique that takes advantage of a common Active Directory misconfiguration of Kerberos accounts with preauthentication disabled. Without ever interacting directly with a user, attackers can request and extract encrypted password hashes, then crack them offline with little risk of detection.
This blog has provided a real-world example of the AS-REP Roasting process, from identifying vulnerable accounts to extracting hashes. More importantly, it has demonstrated how Trellix Helix, powered by the Advanced Correlation Engine (ACE), can detect this low-noise attack early using a combination of:
- Multilayered threat detection leveraging endpoint and network telemetry
- Dual alerting mechanism with atomic and correlated alerts
The ability to correlate alerts isn't just a feature; it's a fundamental requirement for effective threat detection and response. SOC analysts can leverage the ACE correlation engine features to get advanced correlation capabilities that narrate the full story of an attack, reduce false positives, and apply actionable intelligence to further help thwart adversary actions.
To learn more about the Trellix Helix platform, take our product tour to see it in action or visit this page.
RECENT NEWS
-
Mar 02, 2026
Trellix strengthens executive leadership team to accelerate cyber resilience vision
-
Feb 10, 2026
Trellix SecondSight actionable threat hunting strengthens cyber resilience
-
Dec 16, 2025
Trellix NDR Strengthens OT-IT Security Convergence
-
Dec 11, 2025
Trellix Finds 97% of CISOs Agree Hybrid Infrastructure Provides Greater Resilience
-
Oct 29, 2025
Trellix Announces No-Code Security Workflows for Faster Investigation and Response
RECENT STORIES
Latest from our newsroom
Get the latest
Stay up to date with the latest cybersecurity trends, best practices, security vulnerabilities, and so much more.
Zero spam. Unsubscribe at any time.
